Level, our solution for a Steam's Chat Bot
1. Introduction
During our studies in Cognitive Ergonomics of Digital Technologies at the University of Côte d'Azur, Walid Abdelkefi and I, Thomas Rayon, had the opportunity to work on an ambitious project related to one of the largest online video game distribution platforms: Steam. Our interest in user experience and the challenges of interface ergonomics led us to conduct an in-depth study of Steam's usability, a platform used by millions of gamers worldwide.
Our approach was part of a course unit aimed at enhancing our professional skills through user testing. We chose to focus our study on evaluating Steam's interface, asking the question: Does the current interface effectively meet the needs of such a diverse audience as Steam's, composed both of long-time users of the platform and complete novices? Through a series of rigorous tests, we analyzed how these two groups interacted with the site, identified the strengths and weaknesses of the interface, and proposed recommendations to improve the user experience.
However, our work did not stop at critical analysis. Armed with the insights gained from these tests, we decided to take action by proposing a concrete solution to address the issues we identified. This led to the creation of Level, a chatbot designed to assist users in navigating Steam. Level's mission is to make the platform more intuitive and accessible by offering personalized assistance that adapts to the specific needs of each user, whether they are seasoned Steam veterans or newcomers to the platform.
This project, born out of our passion for ergonomics and user interfaces, demonstrates our ability to identify complex problems and design innovative solutions that enhance the user experience. In the following sections, we will detail the steps of our approach, the results obtained, and how we transformed a theoretical analysis into a practical tool for the benefit of Steam users.
2. User Testing on Steam
2.1. Context and Objectives
As a long-time user of Steam, I have become well-acquainted with the platform's intricacies. While my early experiences with Steam were marked by occasional frustrations—especially when navigating its vast catalog or accessing certain features—years of usage have made me proficient in utilizing the platform efficiently. In contrast, my colleague Walid Abdelkefi has had a different experience. Walid, who prefers using other gaming stores, finds Steam less intuitive and often struggles with its interface. This disparity in our experiences led to numerous discussions between us about the platform's usability.
During one such conversation, we realized that our differing levels of comfort with Steam were not unique to us. We recognized that many new users, like Walid, might face significant hurdles when first navigating the platform, whereas seasoned users, like myself, might overlook these challenges simply due to familiarity. This observation sparked the idea for our project: to critically evaluate Steam's usability from both a novice and an expert perspective and to explore how the platform could be improved to better serve all its users.
Our primary objective was to investigate the specific challenges that new users face on Steam and to identify areas where the platform could be made more user-friendly without alienating experienced users. We aimed to design a comprehensive user testing process that would reveal key pain points in the user experience and guide us in proposing targeted improvements.
2.2. Methodology
Our user testing approach was designed to capture the full spectrum of experiences on Steam, from the perspective of both seasoned and novice users. We structured the study in four key phases:
- User Profiling and Recruitment: To understand the diverse user base of Steam, we started by profiling our participants through a detailed questionnaire. This questionnaire helped us identify users with varying levels of familiarity with Steam, ranging from complete novices to those with years of experience on the platform.
- User Testing Scenarios: We developed eight scenarios reflecting common tasks on Steam, such as purchasing games, finding customer support, or exploring special offers. These scenarios were designed to challenge users with different levels of experience, highlighting areas where novices might struggle and where even experts might find inefficiencies.
- Data Collection and Analysis: We recorded the participants' screen activities to analyze their navigation paths and interactions with the platform. Additionally, we gathered verbal feedback during and after the scenarios to gain insights into their thought processes and frustrations.
- Debriefing and Recommendations: After the scenarios, we conducted debriefing interviews to gather comprehensive feedback on the participants' overall impressions of Steam. These interviews were crucial in understanding the emotional and cognitive responses of users to different aspects of the platform.
2.3. Results and Key Insights
The user testing revealed several critical insights into Steam's usability, particularly highlighting the challenges faced by newer users:
- Positive Aspects: Participants, especially the more experienced users, appreciated the extensive content available on Steam and the frequent promotions. The achievement system, which tracks progress across games, was also a popular feature among long-time users.
- Areas for Improvement:
- Navigation Challenges: Novice users frequently reported difficulties in navigating Steam’s interface. They struggled with finding specific features and often felt overwhelmed by the amount of information presented.
- Search Functionality: The search feature, though widely used, was not always effective. Many participants found it challenging to use filters or properly categorize games, especially when dealing with similar genres.
- Interface Clutter: The information-dense interface posed a significant challenge for new users. The lack of clear visual hierarchy and small font sizes made it difficult for them to quickly find what they were looking for, leading to frustration and disengagement.
3. Level, the Steam Chatbot
3.1. Introduction to the Chatbot Concept
After thoroughly analyzing the usability challenges of Steam, Walid and I faced a critical decision. While it was clear that the platform's interface could benefit from certain improvements to enhance the user experience, especially for novices, we also recognized a significant barrier: the strong resistance to change among Steam's vast and dedicated community of long-time users. Many of these experienced users had grown accustomed to Steam's design and were vocal in their opposition to any drastic alterations. We understood that imposing a redesign could alienate this core user base, leading to dissatisfaction and potential backlash.
However, the need to make Steam more accessible to new users was undeniable. We wanted to create a solution that would bridge the gap between maintaining the familiar interface for expert users and providing a more guided, user-friendly experience for newcomers. This led us to the idea of developing Level, a chatbot designed to assist users in navigating Steam without altering the existing interface. Level was conceived not only as a tool for novice users, to help them overcome the initial hurdles of using Steam, but also as an optional aid for expert users, should they choose to take advantage of it.
3.2. Objectives and Features of the Chatbot
The primary objective of Level was to enhance the user experience on Steam by providing personalized assistance that catered to the needs of both new and experienced users. We aimed to design a chatbot that could seamlessly integrate into the existing Steam platform, offering support without disrupting the familiar interface.
Key Features of Level:
- Guided Game Purchases
Level assists users in purchasing games by guiding them through a secure and straightforward process. It asks for the game title, helps filter options by genre, and provides suggestions if the desired game is unavailable. This feature is particularly useful for novice users who may not be familiar with Steam's extensive catalog and search functions.
- Information Retrieval
The chatbot can provide detailed information about specific games, including user reviews, prices, release dates, and genre classifications. This feature helps users quickly access relevant data without needing to navigate through multiple pages on the platform.
- Game Suggestions
For users who are unsure of what to play, Level can offer game recommendations based on preferences like gameplay style (e.g., single-player vs. multiplayer) and genre (e.g., JRPG, action-adventure). This feature is designed to inspire both novice and experienced users who may be looking for something new.
- Support and Troubleshooting
Level also functions as a support tool, guiding users through common issues like locating downloaded games, contacting customer service, or understanding platform features. This helps reduce the frustration that new users often experience when trying to navigate the more complex aspects of Steam.
- Personalized Interaction
To ensure that the chatbot felt approachable and user-friendly, we designed Level with a respectful and engaging personality. It uses polite language, incorporates emoticons, and adapts its responses based on the user's input. This approach was intended to make the interaction feel more human and less mechanical.
3.3. Chatbot Workflow and Decision-Making Process
The development of Level required careful planning of its interaction flow and decision-making logic to ensure that it could effectively respond to a wide range of user queries.
Below is the decision tree used to map out the possible interactions and responses from the Level chatbot.
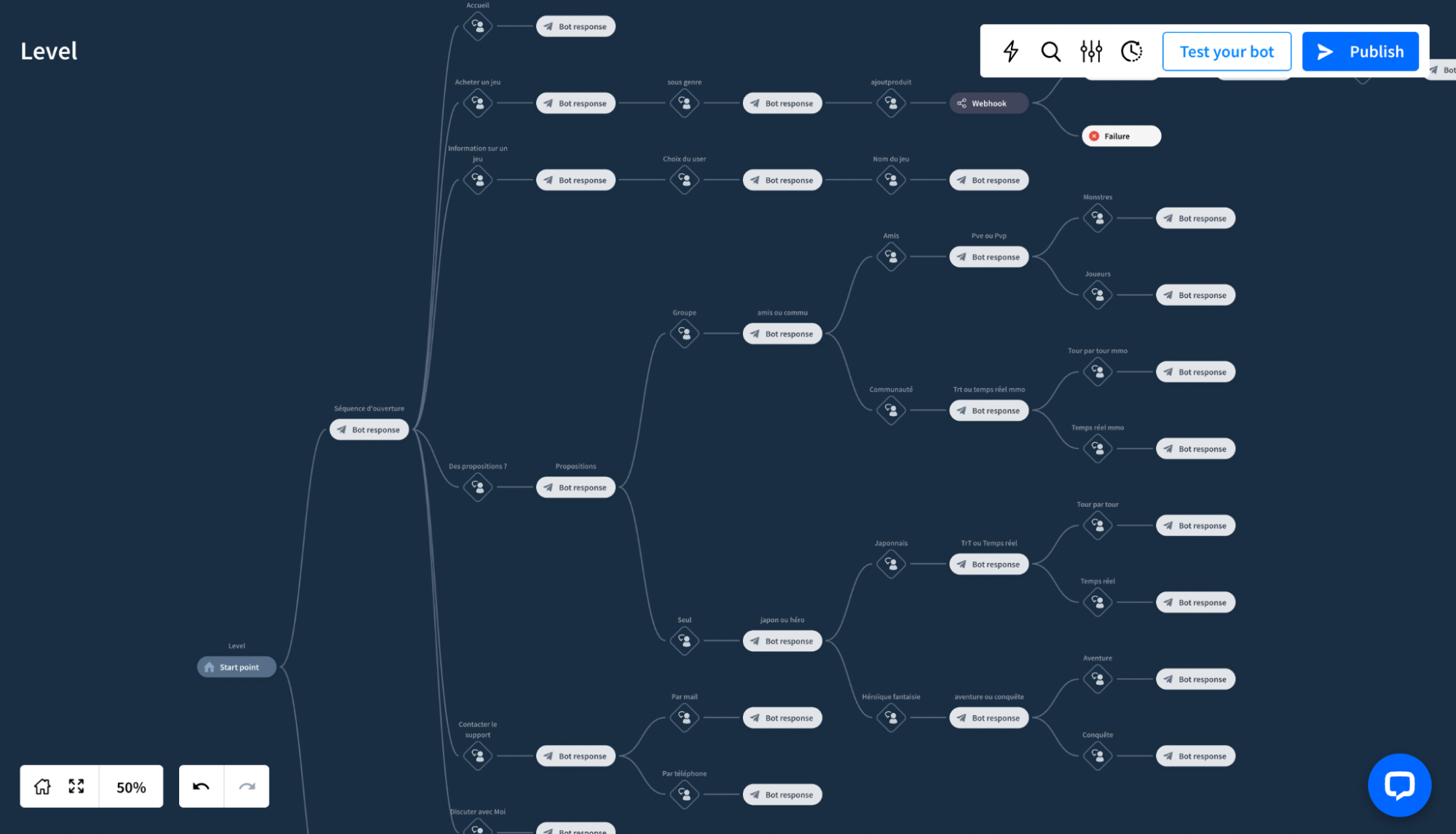
Key Steps in Level's Interaction Workflow:
- Opening Sequence
Upon activation, Level greets the user, introduces its capabilities, and presents options such as buying a game, retrieving information about a game, receiving a game recommendation, or contacting support. This allows users to immediately understand the bot’s functionalities and choose the service they need.
- User Request Handling
Based on the user's selection, Level proceeds with a tailored interaction. For example, if a user wants to purchase a game, Level asks for the game title, checks its availability, and provides relevant options. If the user seeks information, Level narrows down the query to provide precise details.
- Information Filtering
To avoid overwhelming the user with unnecessary information, Level employs a filtering process. For instance, when recommending a game, it asks follow-up questions to refine the user's preferences, such as whether they prefer single-player or multiplayer experiences, and whether they favor certain genres.
- Closing Sequence
Once the user’s request has been fulfilled, Level offers further assistance or concludes the interaction politely, ensuring that the user feels satisfied with the experience. The chatbot also provides quick options to return to the main menu or end the conversation.
3.4. Visual and Interaction Design
To make Level accessible and easy to use, we paid close attention to its visual and interaction design. The chatbot interface was kept clean and simple, with clear prompts and minimal distractions, allowing users to focus on their interaction with the bot rather than the platform's underlying complexities.
Here are some examples of user interactions with the Level chatbot, showcasing its interface and user-friendly design.
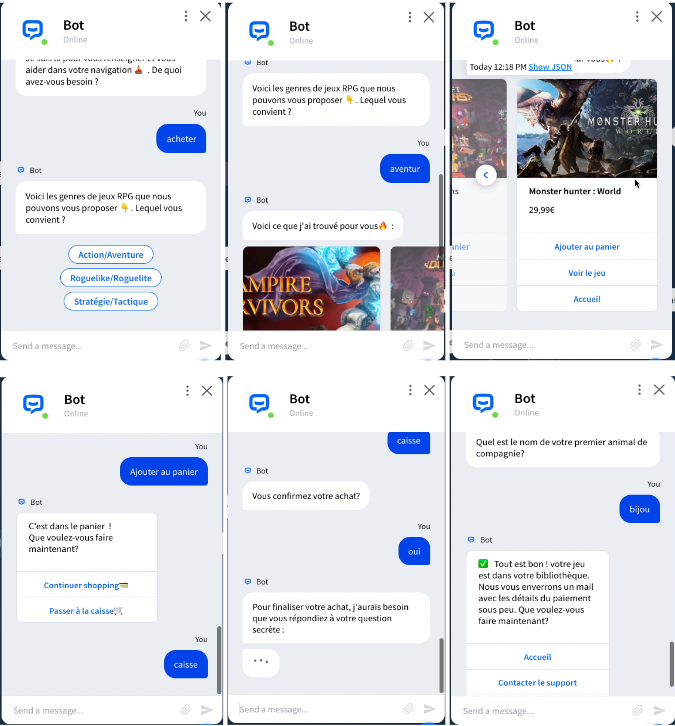
- Visual Elements
Level's interface uses a minimalist design with high contrast for readability. The buttons and text fields are large enough to be easily clickable, even on smaller screens. The chatbot window is unobtrusive and can be minimized or closed at any time, ensuring that it doesn't interfere with the user's main activities on Steam.
- Interactive Responses
The responses from Level are designed to be quick and responsive, ensuring a smooth and engaging user experience. The bot uses dynamic text and icons to make the interaction feel lively and approachable.
4. From Insights to Implementation: Designing Level
4.1. Influence of User Testing Insights on Chatbot Design
The development of the Level chatbot was deeply rooted in the insights we gathered from our user testing on Steam. The challenges faced by both novice and expert users directly informed the functionalities and interaction design of the chatbot, ensuring that it addressed the specific pain points we had identified.
User Testing Insight: One of the primary issues uncovered during our testing was the difficulty new users faced in navigating Steam's complex interface. Many users reported feeling overwhelmed by the dense information and the unintuitive layout of certain features.
Chatbot Design Response: To mitigate these challenges, we designed Level to serve as a guide through Steam’s labyrinthine interface. The chatbot offers step-by-step assistance for common tasks, such as purchasing a game or finding specific information, thereby reducing the cognitive load on the user. This guided interaction ensures that even those unfamiliar with the platform can accomplish their goals without frustration.
Enhancing Search Functionality
User Testing Insight: Our testing revealed that both novice and expert users often struggled with Steam’s search functionality. While experienced users were more adept at finding what they were looking for, novices frequently got lost in the myriad of tags and filters, often resulting in irrelevant search results.
Chatbot Design Response: Level was designed to refine and simplify the search process. Instead of relying solely on Steam’s existing search and filter system, the chatbot engages users in a conversational flow that narrows down options based on their preferences. By asking targeted questions, Level can filter results in a way that feels natural and user-friendly, ensuring that the user is not bombarded with irrelevant information.
Reducing Information Overload
User Testing Insight: Information overload was a significant issue for new users, who often found themselves lost in the sea of options and features that Steam offers. The cluttered interface made it difficult for them to locate the specific functionalities they needed.
Chatbot Design Response: To combat this, we made sure that Level only presented information relevant to the user’s immediate needs. The chatbot’s interaction flow is designed to be concise and focused, guiding users to the exact information or action they require without overwhelming them with unnecessary details. This approach not only streamlines the user experience but also makes Steam more accessible to new users.
Bridging the Expert-Novice Divide
User Testing Insight: While novices struggled with the complexity of Steam’s interface, experts had adapted to it over time and were resistant to any changes. However, both groups could benefit from additional support at times, particularly when dealing with less familiar aspects of the platform.
Chatbot Design Response: Recognizing this, we designed Level to be a flexible tool that caters to both novices and experts. For novices, the chatbot offers a hand-holding experience that simplifies navigation. For experts, Level serves as an optional assistant that can be called upon when needed, ensuring that the bot does not disrupt their established workflows but is available to enhance their experience if desired.
4.2. Learning to Prioritize Research over Immediate Design
One of the most valuable lessons we learned through the development of Level was the importance of thoroughly understanding the problem before jumping into design solutions. In the early stages of the project, we were tempted to quickly move into designing mockups on Figma, driven by the excitement of creating something new. However, our experience with user testing taught us the critical value of deep research and iterative exploration before committing to design.
Importance of Comprehensive User Testing
By spending considerable time on user testing, we were able to uncover nuanced insights that might have been overlooked if we had rushed into design. These insights were crucial in shaping the chatbot’s functionalities and ensuring that it addressed the real needs of users rather than our assumptions about those needs.
Avoiding Premature Design Decisions
Early in the process, we realized that rushing into Figma mockups without fully understanding the user experience would likely result in solutions that only superficially addressed the issues. Instead, we focused on refining the chatbot’s interaction logic and decision trees based on real user data, ensuring that the final design would be both effective and user-centric.
Iterative Development and Feedback Integration
The iterative nature of our development process allowed us to continuously refine Level based on ongoing feedback. Each iteration was informed by the latest insights from our research, ensuring that the design evolved in response to actual user needs. This approach resulted in a chatbot that was not only functional but also genuinely helpful to users, providing a strong foundation for future enhancements.
5. Conclusion
The development of Level was not just about creating a chatbot; it was a comprehensive learning experience that reinforced the importance of research, user testing, and iterative design. By prioritizing these elements over the immediate creation of mockups, we were able to develop a solution that truly addressed the needs of Steam’s diverse user base. This project has significantly shaped our approach to design, teaching us that understanding the problem in depth is the key to developing effective and user-centered solutions.